We are happy to announce IccTA, a new tool for tracking data flows between Android components and even between Android applications. IccTA is a joined work together with Li Li, Alexandre Bartel, Jacques Klein, Yves Le Traon from the University of Luxembourg, Damien Octeau and Patrick McDaniel from the Pennsylvania State University, Steven Arzt, Siegfried Rasthofer and Eric Bodden from EC SPRIDE. IccTA is a tool performing static taint analysis for one or multiple Android applications. It leverages Epicc to connect Android components and FlowDroid to model the life-cycles of components and perform the taint analysis.
The taint analysis is performed intra- and inter-components, which improves the precision of the analysis. IccTA outperforms all other available tools (FlowDroid and AppScan) by reaching a precision of 95.0% and a recall of 82.6% on DroidBench.
When analyzing multiple applications, IccTA first merges them into one then performs the analysis.
Almost exactly the same moment, there came up an additional tool call DidFail from the Carnegie Mellon University, which is a similar approach to IccTA.
IccTA and DidFail both rely on Epicc and FlowDroid to find data leaks between components of Android applications. They can both detect intra- and inter-component leaks within a single application or between multiple applications. Even though they leverage the same tools to compute links between components and perform data-flow analysis, implementation differences result in differences in term of precision.
In the following we would like to do a rough comparison of both tools:
IccTA vs. DidFail:
Currently, FlowDroid does not support callbacks for bound services. DidFail does not support these either since it relies on FlowDroid. On the other hand, IccTA does add its own implementation for bound services callbacks. This can quickly be fixed in FlowDroid, but at the moment lowers the precision of DidFail.
DidFail uses a “path matching” approach. This means that leaks between components cannot be computed in a single step but in two steps. In the first step, partial paths are computed in components (that is from “source” to an “inter-component-method” such as “startActivity” in the first component and from “getIntent()” to “sink” in the second component).
In the second step, partial paths are combined using the path matching approach.
The combinations yield full data flow paths from sources to sinks. The problem is that in some situations the path matching approach over-approximates the number of possible paths. Take the following example:
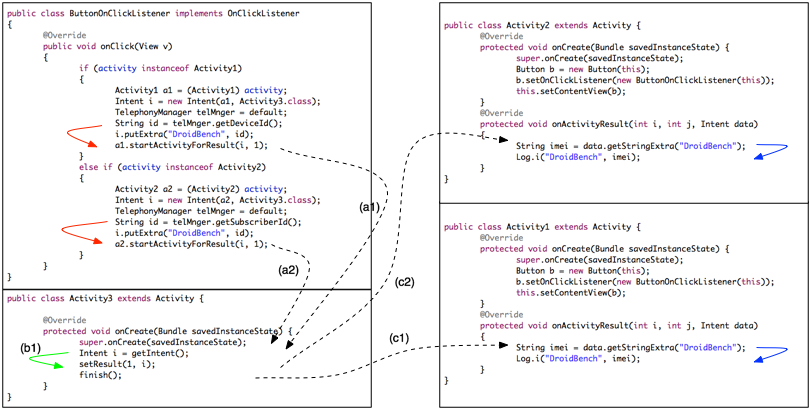
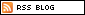
First, let’s start with the intra-component flows:
– ButtonOnClickListener: FlowDroid detects a flow from “getDeviceId()” to “startActivityForResult()” which is an “inter-component-method” (red arrows)
– Activity 3: FlowDroid detects a flow from “getIntent()” to “setResult()” which is also an “inter-component-method” (green arrow)
– Activity 2: FlowDroid detects a flow from “getStringExtra()” to “Log.i()” (blue arrow)
– Activity 1: FlowDroid detects a flow from “getStringExtra()” to “Log.i()” (blue arrow)
Well, this are no news. The news are the ability to track inter-component flows in a really precise way. There are two privacy leaks through inter-component flows:
– (a1) -> (c1)
– (a2) -> (c2)
This is the result of IccTA. Instead, DidFail may produce four privacy leaks (two false positives) since they have a “path matching” approach:
– (a1) -> (c1)
– (a2) -> (c2)
– (a1) -> (c2), false positive
– (a2) -> (c1), false positive
For future work, we will intensive compare both tools to get a better understanding about precision and recall.
(This article was written by Li Li, Alexandre Bartel and Siegfried Rasthofer)
Cross-posted from SEEBlog